Section E17. Limited International Recognition of UN Members and UN Observer States, 2024 Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher
2024 Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher
https://www.rozen-bakher.com/gsr/2024/e/17
Published: 30 April 2024
COPYRIGHT ©2022-2024 ZIVA ROZEN-BAKHER ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher: Yearly Rank to Compare the Global Political Power among Countries, Alliances and Coalitions to Survive Long Wars at the Military, Economic, and Political Levels
Rozen-Bakher, Z. Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher https://www.rozen-bakher.com/gsr
Rozen-Bakher, Z. 2024 Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher, 2024 Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher, 30 April 2024, https://www.rozen-bakher.com/gsr/2024/e
Rozen-Bakher, Z. 2023 Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher, 2023 Global Survival Rank (GSR) by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher, 29 April 2023, https://www.rozen-bakher.com/global-survival-rank-zrb/2023
Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher
Researcher in International Relations and Foreign Policy with a Focus on International Security alongside Military, Political and Economic Risks for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and International Trade
Section E17. Limited International Recognition of UN Members and UN Observer States
Chart 14. Limited International Recognition of UN Members and UN Observer States: Number of Countries that Recognize versus Number of Countries that Do Not Recognize
E17.1 Armenia
The Conflict of Nagorno-Karabakh Triggered the Limited International Recognition in Armenia, yet keep in mind, that The Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh was dissolved in September 2023, despite that, there is still ongoing conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan.
Map 26. Map of Armenia and Azerbaijan
E17.1.1 Limited International Recognition of Armenia Amid the Conflict of Nagorno-Karabakh
Table 111. Comparison of Armenia versus Azerbaijan
E17.1.2 Countries that Formally Don’t Recognise the Sovereignty of Armenia
Map 27. International Recognition of Armenia
Table 112. List of Countries that Don’t Recognize the Sovereignty of Armenia
Table 113. Sovereignty of Armenia: Recognition versus Not Recognition
E17.2 China
China - People's Republic of China (PRC); Taiwan - Republic of China (ROC)
Until the end of WWII, Taiwan was part of the mainland China, while after that, has started the conflict of ‘One China’ between China and Taiwan. Importantly, until 1971, Taiwan ROC was represented China PRC in the United Nations, while after 1971, China PRC started represented itself in the United Nations including Taiwan ROC that lost its vote rights in the United Nations. Since then, very limited number of countries Formally recognized Taiwan as an Independent Country because China cuts diplomatic relations with any country that violate the policy of ‘One China’ by recognizing Taiwan as an Independent Country.
Map 28. Map of China and Taiwan
E17.2.1 Limited International Recognition of China Amid the Conflict of ‘One China’ with Taiwan
Table 113. Comparison of China versus Taiwan
E17.2.2 Countries that Formally Don’t Recognise the Sovereignty of China
Map 29. International Recognition of China
Table 114. List of Countries that Don’t Recognize the Sovereignty of China
Table 115. Sovereignty of China: Recognition versus Not Recognition
E17.3 Cyprus
Cyprus was annexed by Ottoman Empire in 1571 and most of the years after that until 1878, Cyprus was part of the Ottoman Empire. From 1878 until 1960, Cyprus was a Colony of UK, while in 196o, United Cyprus gained independence from UK when Greece and Turkey agreed to abandon their demand for sovereignty on the island, still, UK keeps until today two military bases on the island as two colonies: Akrotiri and Dhekelia. However, in 1974, occurred a coup d'état in trying to annex the island to Greece, which in respond, led to the Turkish invasion of Northern Cyprus. Eventually, in 1983, Northern Cyprus made self-declaration of independence, which until today is recognized only by Turkey.
Map 30. Regional Map of Cyprus
E17.3.1 Limited International Recognition of Cyprus Amid the Conflict of Turkish Northern Cyprus
Table 116. Comparison of Cyprus versus Northern Cyprus and Turkey
E17.3.2 Countries that Formally Don’t Recognise the Sovereignty of Cyprus
Map 31. International Recognition of Cyprus
Table 117. List of Countries that Don’t Recognize the Sovereignty of Cyprus
Table 118. Sovereignty of Cyprus: Recognition versus Not Recognition
E17.4 Israel
The Muslim/Arab-Israeli Conflict started in 1947 when the United Nations approved the Palestine Partition Plan. Since then, repeated wars erupted between the State of Israel and the ‘Muslim-Arab Bloc’ when some countries even sent troops to fight against Israel, while others gave Military Aid, still, in 1979, a ‘Cold Peace Agreement’ was signed between Israel and Egypt that marked the returning of occupied Sinai, yet without returning of Gaza, while in1994, a ‘Cold Peace Agreement’ was also signed with Jordan, yet without returning the occupied of West Bank. Hence, currently, there are two ongoing conflicts between Israel and ‘Muslim-Arab Bloc’: i) The ongoing conflict amid Occupied Palestine that includes the West Bank and Gaza. ii) The ongoing conflict between Israel and Syria amid the Occupied Golan Heights.
Map 32. United Nations Resolution 181 - Partition Plan for Palestine to End the British Mandate by Creation of independent Arab and Jewish States including Special Status for Jerusalem
Map 33. Israel Map after Six-Days War in 1967 that includes the Occupied Territories of Egypt (Sinai and Gaza), Jordan (West Bank), and Syria (Golan Heights)
Map 34. Israel Map since the Peace Agreements with Egypt (1979) and Jordan (1994) that still includes the Occupied Territories of Gaza (Former of Egypt), West Bank (Former of Jordan), and Golan Heights of Syria
E17.4.1 Limited International Recognition of Israel Amid the Muslim/Arab-Israeli Conflict
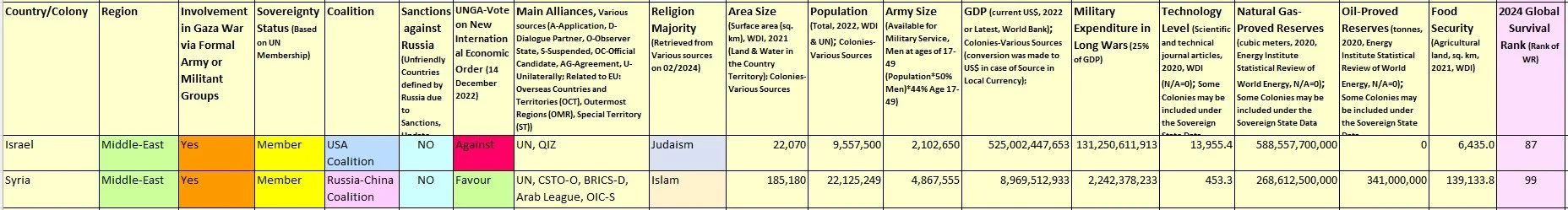
Table 119. Comparison of Israel versus Palestine amid the Israeli Occupation of Gaza and West Bank
Table 120. Comparison of Israel versus Syria amid the Israeli Occupation of Golan Heights
E17.4.2 Countries that Have Ongoing Involvement in Wars with Israel via Formal Army or Militants
Table 121. Countries that Have Ongoing Involvement in Wars with Israel via Formal Army or Militants
E17.4.3 Countries that had Past Involvement in Wars with Israel via Formal Army or Militants
Table 122. Countries that had Past Involvement in Wars with Israel via Formal Army or Militants
E17.4.4 Countries that Currently Formally Don’t Recognise the Sovereignty of Israel
Map 35. International Recognition of Israel
Table 123. List of Countries that Don’t Recognize the Sovereignty of Israel
Table 124. Sovereignty of Israel: Recognition versus Not Recognition
E17.5 North Korea
North Korea - Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK); South Korea - Republic of Korea
At the end of WWII, Korea was divided into two territories namely, the Soviet Union that occupied the North and the USA that occupied the South. Following that, in 1948, two separate countries were established: North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) and South Korea (Republic of Korea). However, in 1950, erupted the Korean War when North Korea invaded South Korea. The Korean War was ended 3 years later via the Korean Armistice Agreement, still, until today, there is ongoing conflict between North Korea and South Korea.
Map 36. Map of North Korea and South Korea
E17.5.1 Limited International Recognition of North Korea Amid the Division of Korea
Table 125. Comparison North Korea versus South Korea
E17.5.2 Countries that Formally Don’t Recognise the Sovereignty of North Korea
Map 37. International Recognition of North Korea
Table 126. List of Countries that Don’t Recognize the Sovereignty of North Korea
Table 127. Sovereignty of North Korea: Recognition versus Not Recognition
E17.6 Palestine
The Israeli-Palestine Conflict started in 1947 when the United Nations approved the Palestine Partition Plan. Following that, repeated wars erupted between the State of Israel and the ‘Muslim-Arab Bloc’ when some countries even sent troops to fight against Israel, while others gave Military Aid. However, in the Six Days War (1967), Israel occupied several territories from Egypt, Jordan and Syria including West Bank and Gaza. In 1979, a ‘Cold Peace Agreement’ was signed between Israel and Egypt that marked the return of occupied Sinai, yet without returning of Occupied Gaza, while in 1994, a ‘Cold Peace Agreement’ was also signed with Jordan, yet without returning the occupied West Bank. Since then, the Israeli-Palestine Conflict has focused on the ‘One-State Solution’ (Israeli Annexation of the West Bank and Gaza) versus the Two-States Solution (Establishment of the State of Palestine as an Independent Country that will include the West Bank and Gaza). Note, Please see Section E17.4.2 for Countries that Have Ongoing Involvement in Wars with Israel via Formal Army or Militants, while Section E17.4.3 for Countries that had Past Involvement in Wars with Israel via Formal Army or Militants.
Map 38. Map of the State of Palestine based on the 1967 Green-Line (International Law), which includes Gaza, West Bank and East Jerusalem
E17.6.1 Limited International Recognition of Palestine Amid the Israeli Occupation of Palestine
Table 128. Comparison Palestine versus Israel
E17.6.2 Countries that Formally Don’t Recognise the Sovereignty of Palestine
Table 129. List of Countries that Don’t Recognize the Sovereignty of Palestine
Table 130. Sovereignty of Palestine: Recognition versus Not Recognition